Displaying 1126 - 1140 of 1291
Evaluation
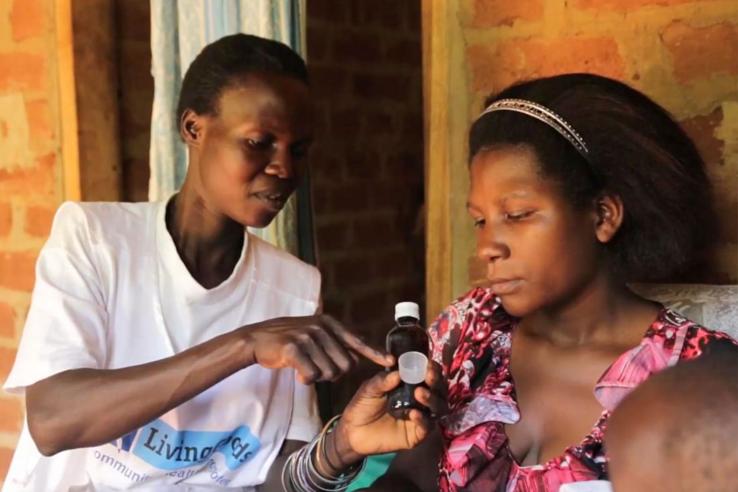
Millions of children die from preventable diseases every year, primarily in low-income countries. In rural Uganda, researchers are working with Innovations for Poverty Action to evaluate the impact on child mortality of an at-scale community health worker program based on a micro-franchise business model. An initial impact evaluation of this program in Uganda found a significant reduction in infant and child mortality, as well as improved health knowledge among clients and an increased number of household visits by health workers. Results from this evaluation of the scaled-up program are forthcoming.
Evaluation
Researchers conducted a randomized evaluation to test whether encouraging entrepreneurs to raise their aspirations helped them improve their financial decisions and outcomes. The aspirations training led individuals to set higher savings goals, but most participants failed to achieve their goals.
Evaluation
Researchers are conducting a randomized evaluation to test the impact of emissions reductions-focused loan support to small and medium firms in Türkiye on reducing these firms’ greenhouse gas emissions and protecting firm growth.
Evaluation
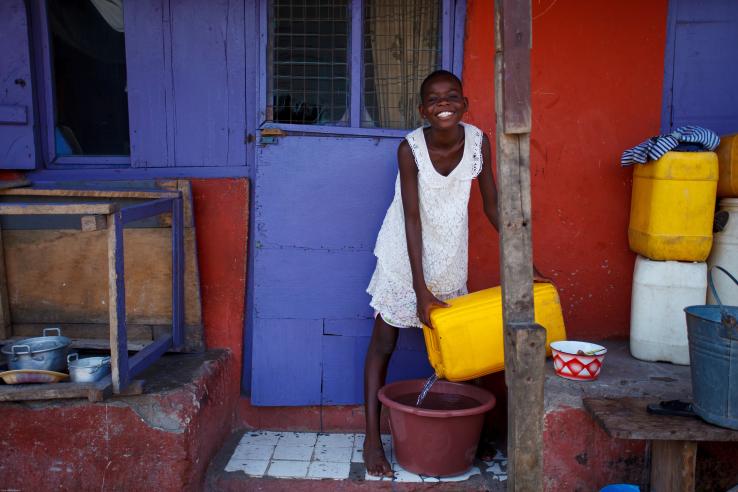
Researchers in Ghana are attempting to measure households' demand for simple ceramic water filters by offering the filter at different price levels through door-to-door sales. They will also explore whether different household characteristics, such as education, income, and health, affect a household's willingness to pay for a filter.
Evaluation
Researchers conducted a randomized evaluation to test the impact and cost-effectiveness of fully online and blended STEM classes in Russia on student test scores. Students in online and blended courses achieved similar scores to students in traditional in-person courses at a lower cost.
Evaluation
Researchers are conducting a randomized evaluation to test the impact of public health messages on hand washing and compliance with government mandated guidelines in Mexico.
Evaluation
Researchers are conducting a randomized evaluation to test the impact of access to credit and business training on entrepreneurs’ business outcomes and households’ resilience to cope with the consequences of COVID-19. Research is ongoing; results are forthcoming.
Evaluation
In partnership with the Ministry of Women and Vulnerable Populations of Peru, researchers are evaluating a text-based campaign designed to help men regulate their emotions and reduce perpetration of IPV during the Covid-19 pandemic.
Evaluation
The Government of Telangana is partnering with researchers to determine the impact of restoring water tanks for irrigation on water management, agricultural output, and farmers’ income.
Evaluation
Researchers in northern Ghana conducted a randomized evaluation to assess the underlying reason for underinvestment by examining the relative effectiveness of cash grants and insurance grants in improving crop yields. Results suggest that uninsured risk, rather than a lack of capital, was the primary constraint on investment. Researchers found that farmers who received free insurance spent more on fertilizer and hired labor, and they also cultivated more land than those who received cash grants.
Evaluation
Researchers evaluated the impact of simplified award letters and different framing and messaging on students’ decision-making in their college selection process and uptake of financial aid. Researchers found that notification letters containing simplified and behaviorally informed language increased Cal Grant account registration but had no impact on eventual take-up of financial aid. Letters that included individualized net cost calculations as well as psychological nudges were found to slightly increase enrollment at community colleges.
Evaluation
Researchers will investigate whether mobilizing local political leaders to strengthen the link between local collections and urban services can increase citizens’ willingness to pay for services, improve service delivery, and ultimately revitalize the social compact.
Evaluation
In India, researchers will evaluate the impact of financial incentives, information, and reminders on treatment regimen compliance among patients of a healthcare provider in the slums of Mumbai.
Evaluation
Employers often rely on subjective performance evaluations by supervisors to gauge the performance of workers–particularly in the public sector, where civil servants’ work performance is hard to measure. However, relying on the opinions of local supervisors could cause subordinates to prioritize pleasing their supervisors rather than focusing on productive tasks and work responsibilities. Researchers conducted a randomized evaluation testing the impact of two alternative subjective performance evaluation schemes on subordinates’ work performance.
Evaluation
Researchers examined the impact of race concordance (when the race of a patient matches that of their physician) and incentives on the take-up of preventive health services by Black men. Results indicate that physician race concordance significantly boosted demand for all preventive health services, and especially for more invasive tests.