Displaying 1921 - 1935 of 8336
Policy insight
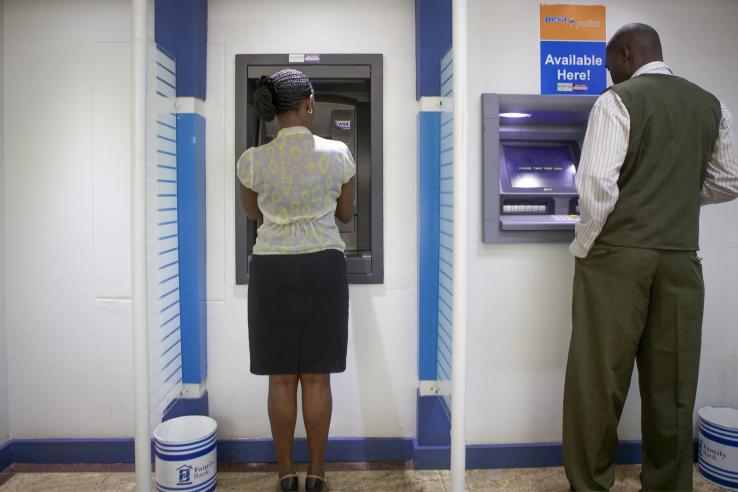
High costs associated with formal bank accounts are often cited as a key obstacle for low-income households to save in formal financial institutions, but lowering the cost of savings does not consistently increase savings flows, likely due to a multitude of other barriers. Given the positive welfare...
Blog
Transitioning from a classroom to an online video conference is challenging for everyone involved—teachers must make extra effort to engage students effectively, and students in turn have to make an extra effort to stay engaged amid distractions at home. Research suggests that students typically do...
Blog
A conversation with TaRL Africa, J-PAL, and the Ministry of National Education of Côte d’Ivoire. Originally posted by the Brookings Institute.
Update
J-PAL Updates
A new study, released today in Science, points to a way to help repair social ties and promote coexistence after war. New findings show that among persecuted Christians in post-ISIS Iraq, playing on soccer teams with Muslim players helped promote more open attitudes toward Muslims, but only Muslim...
Update
J-PAL Updates
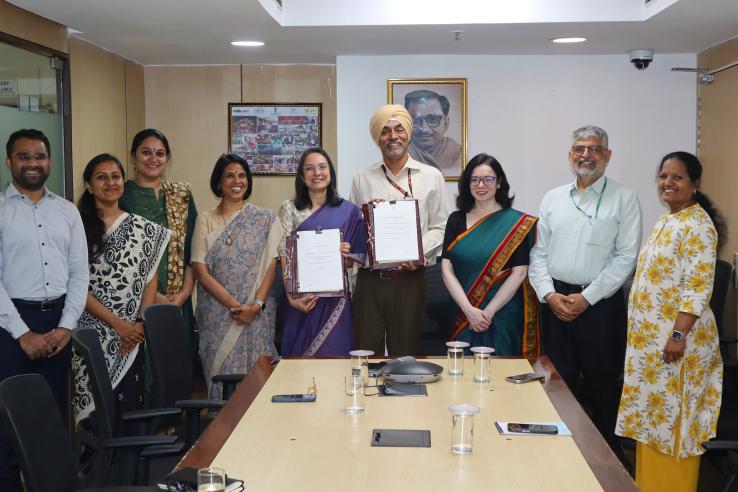
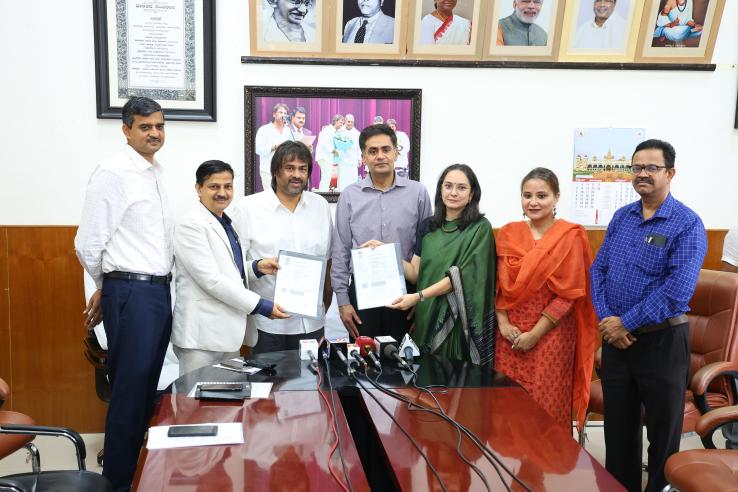
The Government of India’s Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD) has brought the Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL) South Asia at IFMR on board as a knowledge partner on ‘Samaveshi Aajeevika’, a comprehensive livelihoods programme designed to put rural women on the path to self-sufficiency.
Update
J-PAL Updates
The partnership with J-PAL South Asia underscores the Department of School Education and Literacy's strategic, evidence-based approach to strengthen policies.
Research resource
This resource guides researchers through background research and early discussions with a program implementer who has expressed interest in a randomized evaluation, and with whom a partnership seems potentially viable. It provides guidelines for researchers to conduct early conversations with twin...
Person
Apoorva Baheti is a Research Support Assistant at the Haqdarshak project, which aims to leverage technology to improve access to social welfare schemes. Prior to joining in March 2020, she worked as an Actuarial Manager at ICICI Prudential Life Insurance.
Person
Allison Moore is a Junior at MIT from Milwaukee, WI majoring in Economics and Math with Computer Science. At J-PAL, she works on the Bandhan Ultra-Poor projects, coordinating data cleaning with field-based RAs.
Blog
In honor of International Women’s Day this week, we are highlighting insights from a new literature review of the most effective approaches to improving women's agency and sharing ideas for further research.
Research Paper
File: Research paper
Research Paper
File: Research paper
Research Paper
File: Research paper
Research Paper
File: Research paper
Research Paper
File: Research paper