Displaying 796 - 810 of 1291
Evaluation
Researchers introduced four savings devices to estimate the relative importance of different potential barriers to health savings. Results indicate that just providing a safe place to keep money led to a large increase in health savings. These results suggest that simply labeling funds for a specific purpose can help households save and invest more.
Evaluation
Researchers investigated the impact of a new product that allowed Kenyans to invest small amounts of money in low-risk, high-return infrastructure bonds using their mobile phones. However, lack of awareness and low product take-up, triggered by logistical issues during implementation and a pending general election, ultimately led researchers to discontinue the evaluation.
Evaluation
Researchers aim to identify which firms can benefit from engaging with and advertising on digital advertising platforms, to explore the reasons why they may not already be doing so, and to test whether input-based versus results-based approaches are most cost-effective for policy.
Evaluation
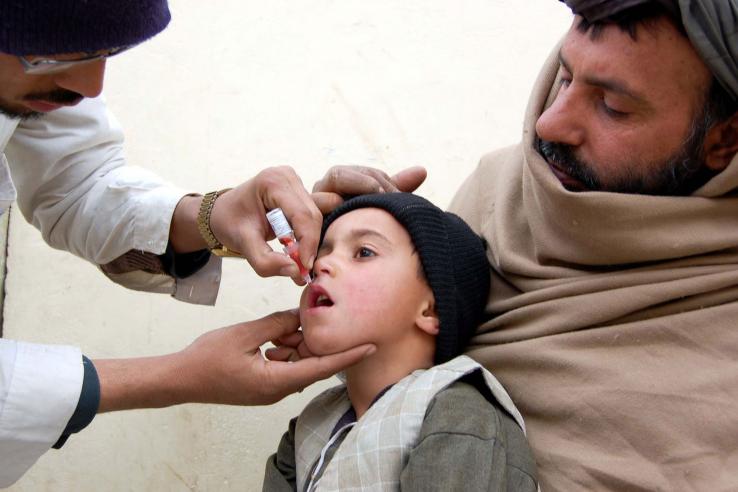
Polio is endemic in Pakistan, and vaccination campaigns often suffer when government health workers hired to administer the vaccine underperform. Researchers introduced individualized bonus contracts to health workers to evaluate the impact of time preferences on vaccine delivery and quality of service. Relative to those with random contracts, vaccinators with tailored contracts provided significantly smoother service.
Evaluation
Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) are thought to be important drivers of growth in developing economies, but entrepreneurs in these countries face many barriers, including poor access to training, finance, and business networks. In Colombia, Fundación Bavaria’s “Destapa Futuro” (Open the Future) program identifies promising enterprises and provides them with a suite of financial, technical, business, and training resources.
Evaluation
In partnership with Jacaranda Health, researchers evaluated a family planning program that provided pregnant women with varying combinations of vouchers for free modern contraception and reminders of the importance of family planning. While none of the combinations increased self-reported use of modern contraception in the short term, the combination of the voucher and reminder did increase its use in the medium term.
Evaluation
Encouraging the adoption of health seeking behaviors remains a challenge today, despite the affordability and availability of health improving technologies and services. Researchers tested whether providing principals in rural primary schools in China with information, school subsidies, and performance based financial incentives reduced the prevalence of anemia in schools. Only schools receiving the financial incentive showed a significant decrease in anemia prevalence; however when pre-existing incentives for educational performance were also present, both the information and the financial incentives were effective in reducing anemia.
Evaluation
Helping families with young children living in high-poverty housing projects to move to lower-poverty neighborhoods improves the later-life outcomes for the children and may reduce the intergenerational persistence of poverty.
Evaluation
In Hong Kong, researchers conducted a randomized evaluation to test the impact of indirectly incentivizing protest participation on sustained participation in a political movement and to identify the role social networks play in protest turnout. Indirectly incentivizing participants to attend a political protest increased their participation regardless of how many of their peers received the same incentive. Participants’ subsequent protest participation remained persistently higher a year later, but only when at least half of their social network was also incentivized to attend the initial protest.
Evaluation
Researchers conducted an evaluation to test the impact of introducing a second school-based nutrition program, and monitoring these two programs, on child nutrition and program implementation. Results showed that high intensity monitoring improved the implementation of the government’s iron and folic acid supplementation program and, in turn, improved child health. The introduction of the new micronutrient mix intervention crowded out implementation of the government’s iron and folic acid supplementation program, leading to no net change in child health.
Evaluation
Researchers conducted a randomized evaluation to determine the effect of a school-based management program, Programa Escuelas de Calidad, on student performance in Mexico. The program combined a cash grant with state support to design and carry out school improvement plans. The intervention did not have any effect on school performance after one year.
Evaluation
Certified teachers were no more likely than non-applicants to be effective at improving students’ test scores, but were more effective than unsuccessful applicants. Researchers found that estimates of teacher effectiveness based on test scores from previous years were a strong predictor of student achievement.