Displaying 901 - 915 of 1291
Evaluation
Many governments and organizations use finance and management training as a tool to promote small and medium enterprise growth in developing countries, but it is not clear whether or how information from these trainings is shared across SMEs operating in the same area.
Evaluation
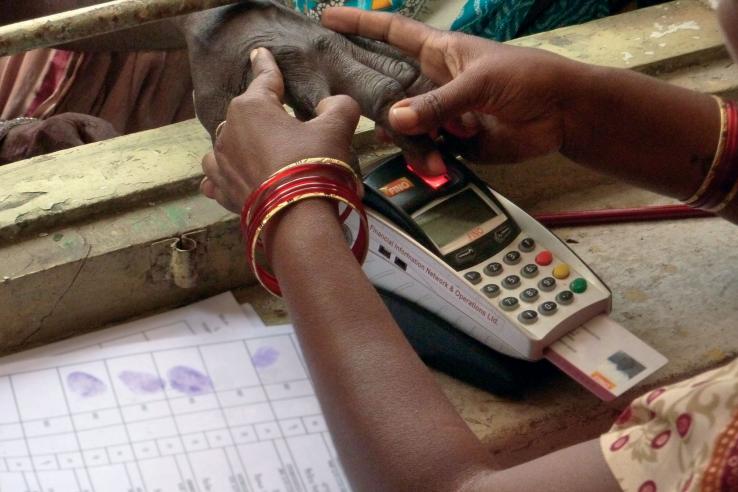
In India, a biometrically authenticated payment system reduced corruption and substantially improved the delivery of government social assistance programs despite partial implementation.
Evaluation
Researchers conducted a randomized evaluation of the impact of the Oportunidades CCT program in Mexico on recipients’ investments decisions and long-run poverty levels. They found that the cash transfers promoted long-term increases in consumption through investment in productive activities, enabling beneficiary households to achieve higher living standards that can be sustained even after transitioning off the program.
Evaluation
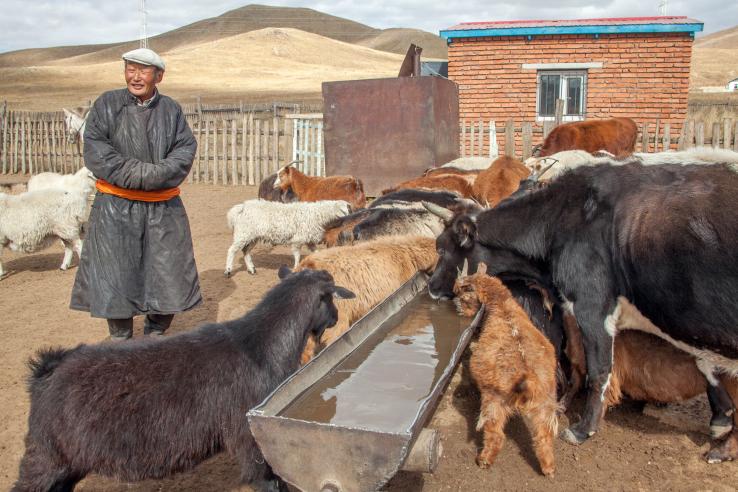
Researchers compared the impacts of providing group- or individual-liability loans to women in rural Mongolia. Access to group loans increased business ownership and food consumption among poor women, while individual loans had no effect on these outcomes.
Evaluation
In Tanzania, researchers examined whether making cash payments conditional on testing negative for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can improve safe sex practices among young adults. They found that offering cash incentives of US$20 significantly reduced STI rates after one year, although smaller incentives of US$10 had no effect.
Evaluation
Early childhood is an important time for both physical and neurological growth and development, but many children fail to reach their development potential. Researchers introduced an early childhood development program in Colombia to test the effects of psychosocial stimulation and micronutrient supplementation on cognitive, behavioral, and physical growth and development. Psychosocial stimulation initially showed positive effects on cognitive growth, although the micronutrient supplementation had no effect. However, a follow-up study showed that the results on cognitive growth disappeared two years later.
Evaluation
Evaluation
Researchers in Mexico evaluated the impact of providing parent associations with larger grants and more information on educational outcomes. Providing information to parent associations reduced students’ disciplinary actions in schools without improving students’ test scores.
Evaluation
In an attempt to reduce employee turnover and increase productivity, companies are increasingly allowing employees to work from home. Researchers analyzed the impact of working from home on productivity and work-life balance by randomly assigning some employees of a call center in China to work from home. Working from home significantly increased employees’ productivity and job satisfaction, although they were less likely to be promoted than similar-performing peers working in the office.
Evaluation
Researchers evaluated the impact of deliberation on voters’ attitudes about two policy issues: airport expansion and revenue sharing. The results indicate that formal on-site deliberations produced changes in attitudes and increased the likelihood that participants would have ordered, consistent preferences, particularly for the less salient policy issue.
Evaluation
School choice programs offer students more opportunities to attend schools with higher achievement and graduation levels. In partnership with the Chicago Public Schools, researchers examined the effects of a school choice program on several traditional student achievement outcomes. They used a randomized lottery to induce school choice and found no measurable difference in traditional education outcomes for students who attended better schools. However, there were some improvements in nonacademic outcomes, such as self-reported disciplinary action and arrests.
Evaluation
Researchers tested the effect of seven different information disclosure messages on credit card clients of a large Mexican bank and found that non-standard information disclosures reduced debt levels and lowered delinquency more effectively than legally mandated disclosures.
Evaluation
Fostering youth entrepreneurship could help decrease youth unemployment. However, entrepreneurs face a number of barriers to launching and expanding their businesses. Researchers introduced a youth entrepreneurship reality TV show to evaluate the effects of a television show and entrepreneurial support activities on viewers’ attitudes, business practices, and employment status.